"@Transaction만 붙으면 자동으로 트랜잭션이 동작하는데 이거 신기하지 않으세요"
멘토링 중 멘토님이 말씀하셨다. 물론 신기하다 허나 왜 그런지 고민해본적이 있었던가..
그냥 당연하듯이 동작할거라는 생각 하에 어떤 원리로 동작하는지에 대한 고민이 부족했기에 공부를 다시 시작했다
이 부분에 대한 깊은 동작 원리나 공부는 추후 토비의 스프링을 공부할 때 배워야겠지만 지금 단계에서는 먼저 프록시 패턴과 트랜잭션이 프록시 패턴과 어떤 연관관계가 있는지 공부해보았다
Proxy Pattern
- 대상 원본 객체를 대리하여 로직의 흐름을 제어하는 행동
- 원본 객체의 수정 없이 제어가 가능하다
구현 코드
public interface IUserController {
User login(String id, String passwd);
User register(String id, String passwd);
}
public class UserController implements IUserController {
@Override
public User login(String id, String passwd) {
return null;
}
@Override
public User register(String id, String passwd) {
return null;
}
}
public class UserControllerProxy implements IUserController {
private UserController userController;
public UserControllerProxy(UserController userController) {
this.userController = userController;
}
@Override
public User login(String id, String passwd) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
User user = this.userController.login(id, passwd);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(endTime - startTime);
return user;
}
@Override
public User register(String id, String passwd) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
User user = this.userController.register(id, passwd);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(endTime - startTime);
return user;
}
}
- 상속이나 인터페이스를 통한 프록시 패턴의 구현은 반복되는 코드가 발생될 수 있다
- 동적 프록시를 통해서 이를 해결할 수 있다
동적 프록시 생성
public class MetricControllerProxy {
public Object createProxy(Object proxiedObject) {
Class<?>[] interfaces = proxiedObject.getClass().getInterfaces();
DynamicProxy dynamicProxy = new DynamicProxy(proxiedObject);
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(proxiedObject.getClass().getClassLoader(), interfaces, dynamicProxy);
}
private class DynamicProxy implements InvocationHandler {
private Object target;
public DynamicProxy(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//동적 메소드 호출
Object result = method.invoke(target, args);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(endTime - startTime);
return result;
}
}
}
@Transaction 동작원리
- JDK에서 제공하는 동적 프록시가 아닌 cglib라는 라이브러리를 사용
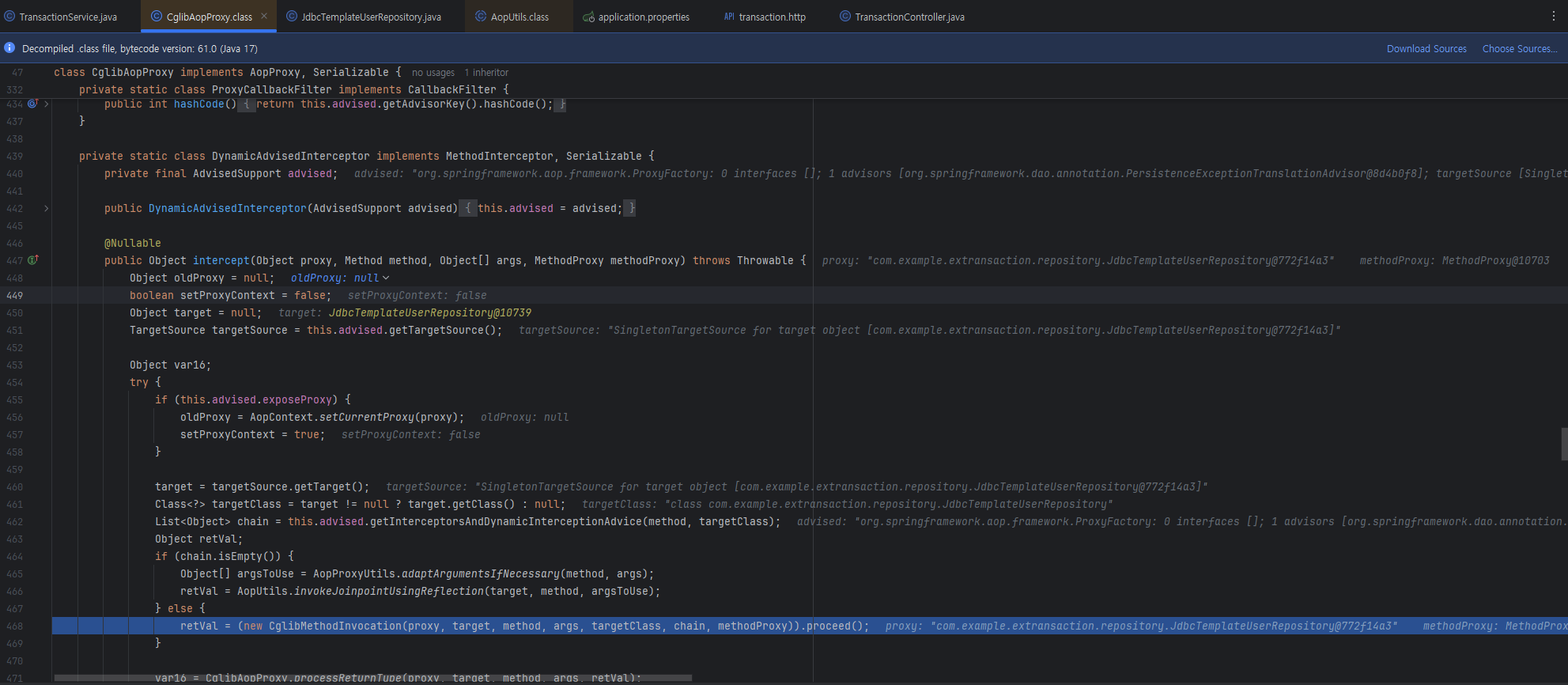
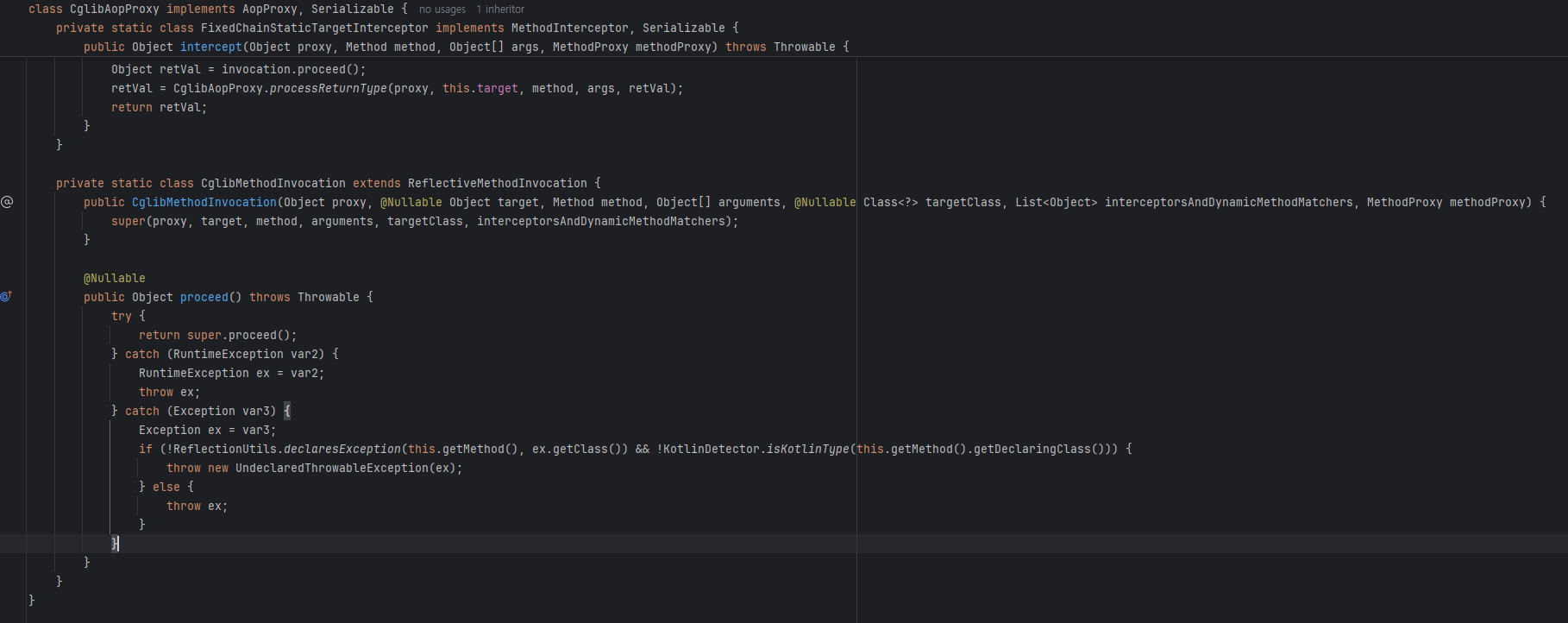
중요한 건 동적 프록시가 대신 하는 행위가 동일하다는 점이다
CGlib vs JDK 프록시
- JDK 프록시는 인터페이스 구현체에 대해서만 프록시 구현이 가능
- CGLIb Proxy는 클래스 상속을 이용하기 때문에 인터페이스가 존재하지 않아도 가@Transaction 동작원리
- JDK에서 제공하는 동적 프록시가 아닌 cglib라는 라이브러리를 사용
- JDK 프록시는 인터페이스 구현체에 대해서만 프록시 구현이 가능
- CGLIb Proxy는 클래스 상속을 이용하기 때문에 인터페이스가 존재하지 않아도 가능!
실제로 트랜잭션을 프록시하는 패턴을 간단한 예제로 만들어보았다
1) 시나리오
- 계좌 서비스 실행
- 송금 / 충전 기능
- Transaction begin (콘솔 출력)
- 비즈니스 로직
- Transaction commit or rollback
- 응답
2) 리팩터링
- 계좌 서비스 프록시 (Transaction 을 해주는 애)
- 실제 송금 / 충전 구현체
- 비즈니스로직 구현
- 트랜잭션은 프록시에 의해 실행
시나리오 코드
public class Account {
private double balance;
public Account() {
this.balance = 0;
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void draw(double amount) {
balance -= amount;
System.out.println("**** draw ****" + balance);
}
public void deposit(double amount) {
balance += amount;
System.out.println("**** deposit ****" + balance);
}
}
public class AccountService {
Account account;
AccountService(Account account) {
this.account = account;
}
public void draw(int amount) {
try {
System.out.println("TRANSACTION BEGIN");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (amount < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Amount cannot be negative");
}
if (this.account.getBalance() <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Balance is negative");
}
this.account.draw(amount);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(endTime - startTime);
System.out.println("TRANSACTION COMMIT");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("ROLL BACK");
}
}
public void deposit(int amount) {
try {
System.out.println("TRANSACTION BEGIN");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (amount < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Amount cannot be negative");
}
this.account.deposit(amount);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(endTime - startTime);
System.out.println("TRANSACTION COMMIT");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("ROLL BACK");
}
}}
## 구현
public class TransactionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AccountService accountService = new AccountService(new Account());
accountService.deposit(1000);
accountService.draw(1000);
}
}
프록시 패턴을 적용한 사례 (리팩토링)
public interface AccountInterface {
void draw(int amount);
void deposit(int amount);
}
//기존 섞여있는 코드에서 비즈니스 코드만 포함
public class AccountService implements AccountInterface {
Account account;
AccountService(Account account) {
this.account = account;
}
public void draw(int amount) {
if (amount < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Amount cannot be negative");
}
if (this.account.getBalance() <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Balance is negative");
}
this.account.draw(amount);
}
public void deposit(int amount) {
if (amount < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Amount cannot be negative");
}
this.account.deposit(amount);
}
}
public class AccountProxy implements AccountInterface {
private final AccountInterface accountService;
AccountProxy(AccountInterface accountService) {
this.accountService = accountService;
}
@Override
public void draw(int amount) {
try {
System.out.println("TRANSACTION BEGIN");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//분리된 코드 실행
this.accountService.draw(amount);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(endTime - startTime);
System.out.println("TRANSACTION COMMIT");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("ROLL BACK");
}
}
@Override
public void deposit(int amount) {
try {
System.out.println("TRANSACTION BEGIN");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//분리된 코드 실행
this.accountService.deposit(amount);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(endTime - startTime);
System.out.println("TRANSACTION COMMIT");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("ROLL BACK");
}
}
}
public class TransactionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AccountInterface accountService = new AccountService(new Account());
AccountProxy proxy = new AccountProxy(accountService);
proxy.deposit(1000);
proxy.draw(1000);
}
}
- 프록시를 적용했음에도 여전히 중복되어있는 코드가 발생되었다
- 추후 유지보수가 힘들 가능성이 높아 동적프록시를 적용해보았다.
JDK 동적 프록시를 사용한 예시
public class TransactionInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private Object target;
TransactionInvocationHandler(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
try {
System.out.println("TRANSACTION BEGIN");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//분리된 코드 실행
result = method.invoke(target, args);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(endTime - startTime);
System.out.println("TRANSACTION COMMIT");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("ROLL BACK");
}
return result;
}
}
public class TransactionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AccountInterface accountService = new AccountService(new Account());
AccountInterface proxy = (AccountInterface) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
accountService.getClass().getClassLoader(),
accountService.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new TransactionInvocationHandler(accountService)
);
proxy.deposit(1000);
proxy.draw(1000);
}
}
'BackEnd > Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 스프링/자바 동작 순서 (0) | 2024.10.07 |
|---|---|
| [Spring] 스프링 MVC Dispatcher Servlet (1) | 2023.04.05 |
| 애노테이션으로 유효성 검토 (0) | 2022.12.19 |
| 스프링 빈의 멤버변수는 ThreadSafety하지 않다. (0) | 2022.12.19 |

